How Insulated Water Bottles Keep Drinks Hot or Cold: A Buyer’s Guide for Brands and Distributors
You’ve probably heard of YETI bottles—they keep drinks hot for 12+hours, even during long outdoor adventures. On the other hand, you might have received a branded giveaway insulated water bottles that seems to lose its temperature after just 6 hours, leaving users frustrated and unlikely to use it again. How is it that two bottles with the same vacuum structure can perform so differently when it comes to insulation?
The answer lies in more than just the vacuum itself. From the type of reflective lining to the quality of the seal and the materials used, every detail affects how long a bottle can maintain its temperature. For brands and bulk buyers, understanding these differences is key—not only to provide a better experience for end users, but also to make smart decisions when designing or sourcing custom insulated bottles.
Table of Contents
Toggle3 Insulation Principles that Insulated Water Bottles Keep Drinks Hot
Insulated water bottles rely on a combination of clever engineering and material choices to maintain beverage temperature for hours. The first key element is the vacuum layer: by creating a space with almost no air between the inner and outer walls, the bottle prevents heat from transferring through conduction or convection. This is why a properly vacuumed bottle can keep hot drinks hot and cold drinks cold far longer than a regular cup.
The second element is the reflective layer. Many high-quality insulated water bottles include an aluminum foil or copper coating that lines the vacuum space or inner walls. This reflective surface bounces heat back into the liquid, reducing energy loss from radiation. In other words, it acts like a mirror for heat, keeping warmth in and cold out—or vice versa.
Finally, sealing and material choice play a crucial role. A well-designed lid and precise sealing prevent air and moisture from escaping, while a durable stainless steel body minimizes heat transfer. Together, these factors create the “triple defense” that allows insulated bottles to deliver consistent temperature performance over time.
3 Factors that lead Different Insulation performance
Even when two bottles use the same vacuum technology, their insulation performance can vary widely. While the vacuum layer is essential for blocking heat transfer through conduction and convection, other factors significantly affect how long a bottle can keep drinks hot or cold.
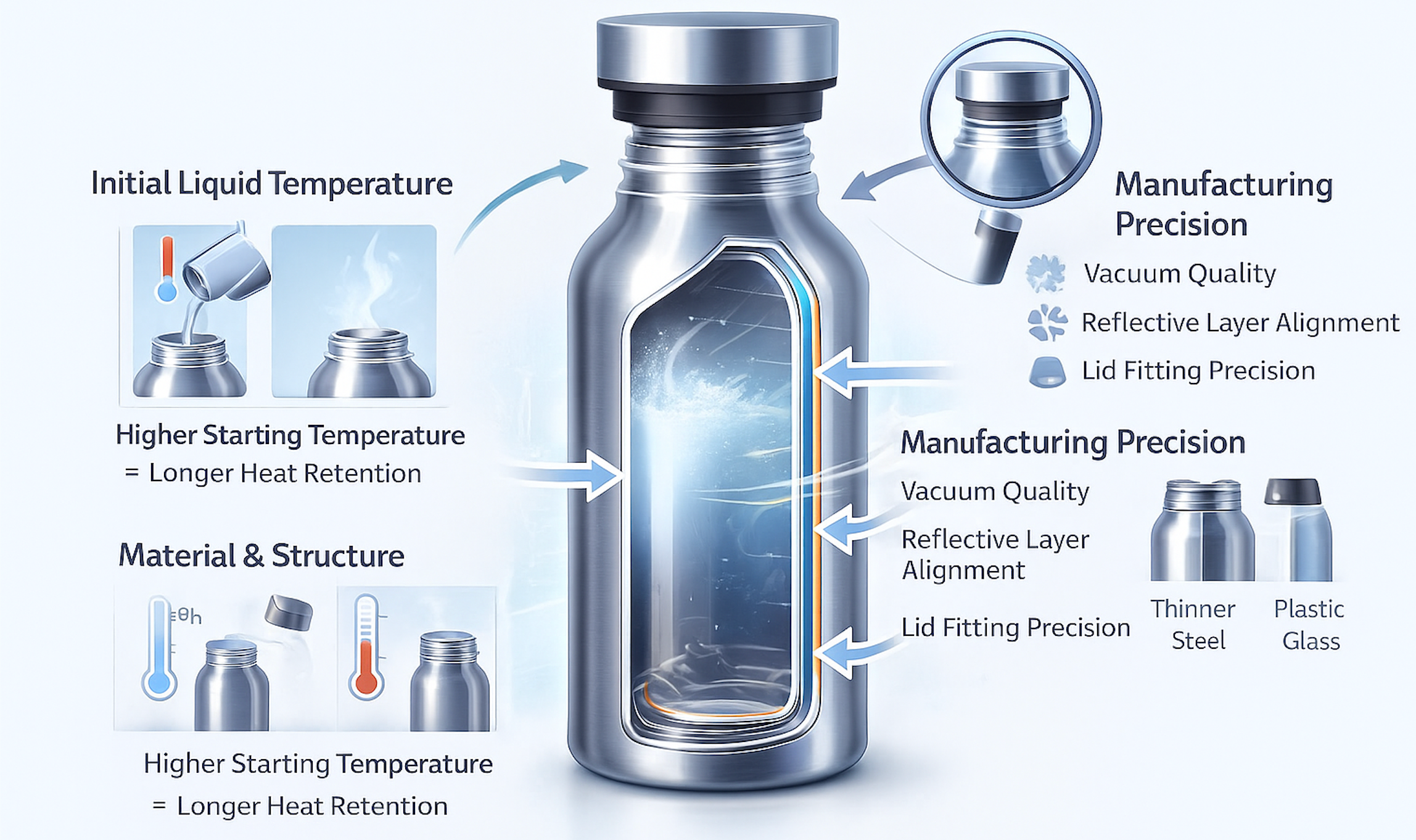
One major factor is the initial temperature of the liquid. Pouring near-boiling water into a pre-warmed bottle will retain heat much longer than filling a cold bottle with the same water. Similarly, chilled beverages last longer in a pre-cooled bottle. This simple step can make a noticeable difference in real-world performance.
Other critical factors include inner liner material, wall thickness, and lid design. Stainless steel retains heat better than glass or plastic, while thicker walls provide additional insulation. The lid’s sealing quality and type can also greatly impact heat retention—air escaping through a loose or poorly designed cap allows hot or cold air to escape, shortening the effective insulation time.
Finally, manufacturing precision matters. Even small variations in vacuum quality, reflective layer placement, or lid fitting can lead to significant differences in temperature retention between seemingly identical bottles. For brands and buyers, understanding these variables is key to choosing or designing insulated bottles that reliably meet performance expectations.
How Manufacturing Process & Craftsmanship Affect Insulation Performance
When it comes to real‑world insulation performance, the devil is in the details. Even bottles that claim to use vacuum insulation can exhibit very different temperature retention — depending on how they are made. Below are the critical manufacturing and craftsmanship factors that significantly influence how long a bottle can keep drinks hot or cold.
1. Reflective Lining (Aluminum Foil / Copper Coating)
In high‑performance bottles, a thin reflective layer (often aluminum foil, or sometimes metal coatings like copper plating) is added on the inner wall or inside the vacuum layer. This layer acts as a “thermal mirror,” reflecting radiant heat back into the liquid, reducing heat loss via radiation.
The process of installing this lining requires precision: the foil must be shaped, placed flush against the inner liner, then the outer shell sealed before vacuuming. If the foil is crumpled, misaligned, or deformed, its reflective capabilities drop — compromising insulation.
Compared to simply relying on vacuum alone, this extra step of adding a reflective layer can meaningfully extend temperature retention time.
2. Material Quality — Inner Shell & Outer Shell Matter
Usinghigh‑quality, food-grade stainless steel (e.g. 304 stainless steel) for both inner liner and outer shell is important. Such steels resist corrosion, maintain structural integrity, and support stable vacuum insulation over time.
Inferior materials or substandard steel may degrade over time (e.g. rust, warping, loss of sealing integrity), reducing insulation reliability, so 316 stainless steel is preferred for high-end bottles.
Good material choice also supports the manufacturing processes (welding, sealing, vacuuming) that must withstand stress and maintain tight tolerances for long-term performance.
3. Welding / Sealing Quality
The vacuum insulation only works when the gap between inner and outer walls remains airtight. That depends heavily on how well the bottle is welded or sealed. Any tiny leak — even microscopic — can allow air to seep in over time, undermining the vacuum and degrading insulation.
Many high-end insulated water bottles use advanced welding or soldering techniques. For example, lead‑free soldering processes (or specialized vacuum brazing furnaces) are used to weld joints in a way that prevents unwanted contaminants and ensures stable, long-lasting seams.
A robust welding process is especially important for OEM and ODM custom orders for brands — because inconsistencies across units can lead to large variations in insulation performance.

4. Production Precision & Quality Control
From shaping the inner liner and outer shell, to trimming, welding, bottleneck threading, to vacuum drawing, each step must be precisely controlled. Slight deviations — uneven wall thickness, imperfect welds, misaligned reflective foil — can all impact insulation results.
Thorough quality control — for example vacuum integrity testing, leak tests, and heat-retention testing — helps ensure that every bottle meets performance standards, not just a few samples. As noted by professional manufacturers, insufficient QC is a common reason “vacuum bottles” fail to deliver promised insulation times.
5. Insulation Enhancements
Some bottles combine vacuum + reflective lining + additional insulation techniques (e.g. special coatings, multi-layer walls, advanced sealing designs) to push thermal performance further.
For example, inner-wall copper plating and aluminum foil are is used in premium models , with 316 stainless steel for the interior to maximize reflectivity and further cut heat radiation loss.
Such combined enhancements increase manufacturing complexity and cost — but can yield substantial gains in temperature retention, a worthwhile trade-off for premium customized bottles or brand-grade products.
How Cap Design Affects Insulation Performance in Insulated Water Bottles
Even with the best vacuum and reflective lining, a bottle’s insulation performance can be greatly affected by its cap. Heat or cold can escape through poorly designed lids, and the cap type determines how long your beverage stays at the desired temperature. For brands and bulk buyers, understanding cap design is crucial when specifying or sourcing insulated bottles.
Key Cap Types and Their Impact on Temperature Retention
| Cap Type | Seal Quality | Typical Insulation Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Screw Cap | Medium | Long | Basic twist-on lid; simple seal prevents most leaks but may allow slow heat/cold escape. |
| Double-Lock Lid | High | Very Long | Lids with additional locking mechanism or silicone gaskets; excellent airtightness and minimal thermal loss. |
| Vacuum Lock or Straw Lid | Very High | Extremely Long | Advanced lids with vacuum lock or built-in sealing systems; minimizes air exchange, maximizes heat/cold retention. |
Practical Notes for Buyers:
- Even a small leak in the lid can dramatically reduce insulation performance, no matter how advanced the vacuum or lining is.
- Silicone gaskets, double-lock designs, and precision threading improve airtightness and ensure consistent temperature retention.
- When ordering custom or bulk bottles, specifying the cap type and seal quality is as important as specifying material or vacuum quality.
By choosing the right cap design, brands can ensure that end users enjoy a longer-lasting hot or cold beverage experience, which increases satisfaction and brand reputation.
Choosing the Right Insulated Water Bottle for Your Needs
If insulation duration matters for your customers or product line, selecting the right bottle requires evaluating more than just “vacuum.” Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Bottle Material
Choose food-grade 304 or 316 stainless steel with appropriate wall thickness. High-quality steel ensures structural stability, long-term vacuum retention, and safe daily use.
2. Vacuum & Reflective Layer Quality
A stable vacuum layer is essential, but so is a complete reflective lining. Bottles with aluminum foil or copper-coated insulation layers significantly reduce heat radiation loss and maintain temperature longer.
3. Cap Design
The lid plays a decisive role in insulation performance. Choose high-seal designs such as double-lock lids, silicone-gasket lids, or advanced airtight caps that prevent heat exchange.
4. Capacity & Usage Scenario
Larger bottles may lose heat slightly faster due to increased surface area. Consider your usage scenario—outdoor travel, gym, office, daily commuting—to balance insulation time and portability.
Selecting the right combination of material, vacuum integrity, reflective lining, and lid structure ensures that the bottle you choose meets real-world insulation expectations.
Recommendations
Insulation performance in a bottle is never determined by a single feature. It’s the result of vacuum quality, reflective lining, material selection, and lid sealing working together as one system.
For brand owners and buyers, we recommend:
Design your insulated water bottle based on realistic insulation needs rather than generic claims.
Higher insulation requirements mean more complex processes (better stainless steel, stronger lids, reflective layers, enhanced sealing, or specially designed cap)—all of which increase manufacturing cost.
Make smart trade-offs based on your market positioning, usage scenarios, and target customers.
At Haers, we specialize in manufacturing and customizing the best insulated water bottles. Our team helps brands balance cost and insulation effectiveness, ensuring the final product meets both performance expectations and budget requirements.












